Regenerative Endodontics: Saving Teeth with Stem Cells
Stem cells play a
demanding role in development and in
tissue regeneration. The dental pulp contains a small sub-population of stem
cells that are involved in the response of the pulp to caries progression. Odontoblasts replaced by stem cells that have
undergone cell death as a consequence of the cariogenic challenge. Stem cells
also secrete factors that have the potential to enhance pulp vascularization
and provide the oxygen and nutrients required for the dentinogenic response
that is typically observed in teeth with deep caries. Angiogenic factors,
contribute to the demise of the pulp by enhancing vascular permeability and
interstitial pressure required for dentin regeneration. Recent studies focused
on the biology of dental pulp stem cells revealed that the multipotency and
angiogenic capacity of these cells could be exploited therapeutically in dental
pulp tissue engineering.
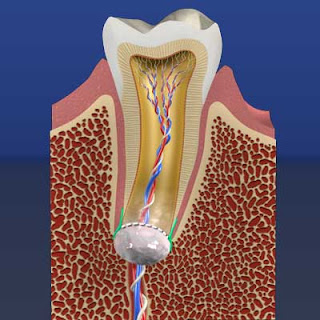
The regenerative
potential of adult stem cells is directed toward achieving the following:
·
Regeneration of damaged coronal dentin
and pulp
·
Periodontal regeneration
·
Repair and replacement of bone in
craniofacial defects
·
Whole tooth regeneration.
Stem cells in endodontic therapy
v Stem cells in the dental pulp:
The fraction of multipotent stem cells in the dental pulp is small and the location
of these cells is not clearly known. SHED having higher proliferative rate than
DPSC due to the presence of large amount of alkaline phosphatase activity and
osteocalcin production.
v Stem cells and caries-induced
dentinogenesis: The dental pulp is a highly
vascularized and innervated connective tissue responsible for maintaining the
tooth vitality and able to respond to injuries. The odontoblasts,
ecto-mesenchymal derived cells, are the first cells to respond to the injury
caused by bacterial invasion during caries progression. A dentin matrix secreted
by primary odontoblast that mineralizes as reactionary dentin in response to
shallow caries.
v Stem cells and pulp angiogenesis:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent inducer of endothelial
cell differentiation and survival, and it is the most effective angiogenic
factor. VEGF also plays a critical role on the control of vascular permeability
during physiological and pathological events.
Application
of stem cells in regenerative Endodontics:
Ø Implantation
Ø Pulp
revascularization
Ø Whole
tooth regeneration
Stem cells are most
important for the physiology of the dental pulp and for the response of this
tissue to injury. These cells may become the primary strategy for the
revitalization of necrotic immature permanent teeth. Such discoveries have the
potential to fundamentally change the paradigms of conservative vital pulp and
root canal therapy, and perhaps allow for the treatment in the future of
conditions that are presently untreatable in Dentistry.


Teeth must be internally strong to remain white and beautiful for long life. My friend is planning is go for braces from dentist Manhattan Beach maybe. As everyone is recommending her to go for the same due to their durability and superb results. Also the dental insurance is in her mind before to cut some more cost. Hoping for the best.
ReplyDeleteThanks for taking the time to share this informative information with us. I really enjoyed going over this article that you provided with all the details that you provided. Have a great rest of your day.
ReplyDeleteDentist Philadelphia
کلینیک دندانپزشکی clinicminimal با تمرکز بر طراحی و اجرای درمان های دندانپزشکی سعی در بازگرداندن لبخند بیماران به روشی زیبا و طبیعی دارد. استفاده از فناوری های پیشرفته و مواد با کیفیت بالا باعث می شود تا نتایج دقیق و جذابی حاصل شود. با توجه به جزئیات و درک نیازهای فردی هر بیمار، این کلینیک درمان های سفارشی را ارائه می دهد که به افزایش اعتماد به نفس و ایجاد لبخندی زیبا کمک می کند.
ReplyDelete